Dealing with Patellar Luxation in Dogs
health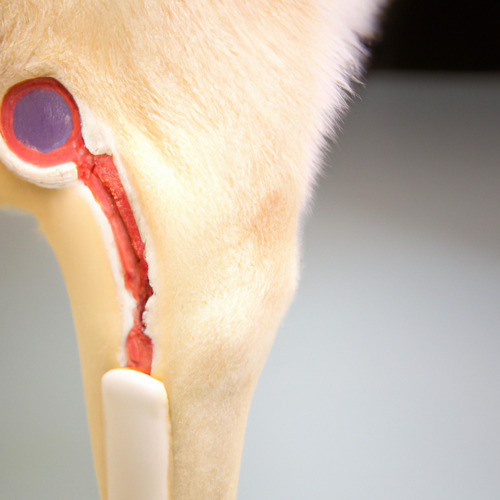
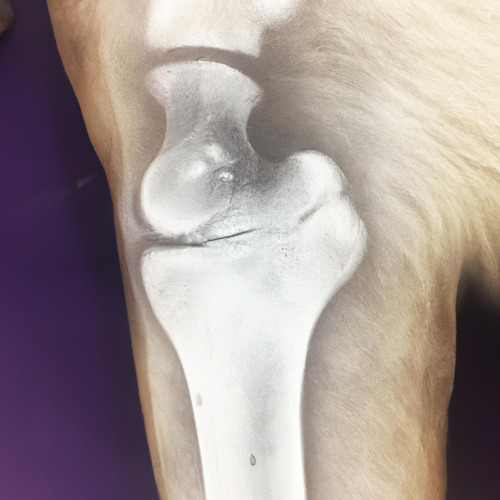
Patellar luxation is a condition that affects the knee joint of dogs and can cause pain, lameness, and other problems. The knee joint is made up of three bones: the thigh bone (femur), the shin bone (tibia), and the knee cap (patella). In a healthy joint, the patella sits in a groove on the end of the femur and slides smoothly as the dog moves.
Cause of Patellar Luxation
However, in dogs with patellar luxation, the knee cap becomes unstable and can slip out of place. This can happen on one or both hind legs and can occur suddenly or gradually over time. The severity of the luxation can vary, ranging from mild to severe, and can affect the dog's ability to walk and perform normal activities.
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of patellar luxation, including:
- Genetics: Some breeds of dogs, such as Pomeranians and Chihuahuas, are more prone to this condition due to their conformation.
- Trauma: Accidents or injuries that affect the knee joint can increase the risk of patellar luxation.
- Overuse: Repetitive jumping, running, or playing can put excessive stress on the knee joint, leading to instability.
Early Signs and Symptoms
The early signs of patellar luxation may include:
- Lameness: This can range from mild to severe, depending on the severity of the luxation.
- Skipping: The dog may start to skip or hop on the affected leg, trying to compensate for the pain.
- Weakness: Over time, the affected leg may become weaker, leading to an obvious limp even when walking at a slow pace.
Diagnosis and Treatment
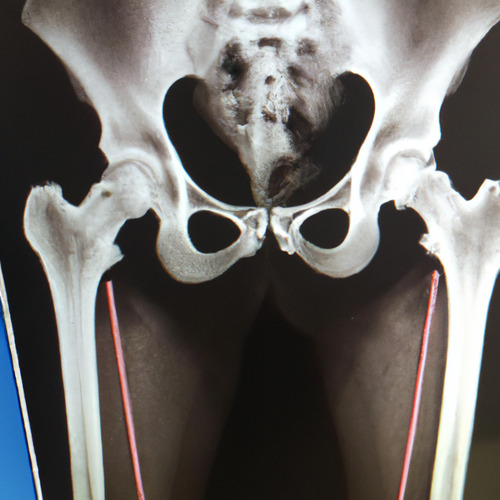
If you suspect your dog may have patellar luxation, it's important to seek veterinary care as soon as possible. The vet will perform a physical examination and may take X-rays to confirm the diagnosis. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to correct the problem and alleviate pain.
In addition to surgery, other treatments for patellar luxation may include:
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs can help reduce pain and swelling in the knee joint.
- Physical therapy: Gentle exercises and stretches can help improve joint mobility and strength.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the stress on the knee joint and slow the progression of the condition.
Prevention and Prognosis
Prevention is key when it comes to patellar luxation. While there is no surefire way to prevent this condition, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk, including:
- Avoiding excessive jumping: Limit the amount of jumping and stair-climbing your dog does, especially if they are a small breed.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Keeping your dog at a healthy weight can reduce the stress on their knees and prevent the progression of the condition.
- Regular check-ups: Regular veterinary check-ups can catch any early signs of trouble, allowing for prompt treatment.
Patellar luxation can be a painful and debilitating condition for dogs, but with proper care and attention, it can be managed. If you suspect your dog may be affected, don't hesitate to seek veterinary care. With the right treatment and support, your furry friend can lead a happy, healthy life.